Acrylonitrile
Acrylonitrile Specification
- Storage
- Store below 30C in tightly closed containers, away from heat, sparks, and open flames
- Purity
- 99% min
- Physical Form
- Liquid
- Properties
- Colorless, volatile liquid with a pungent odor; highly flammable; polymerizes readily in presence of alkalis;
- Density
- 0.806 Gram per cubic centimeter(g/cm3)
- Refractive Rate
- n20/D 1.3914
- Taste
- Bitter, Unpleasant
- Molecular Formula
- C3H3N
- Structural Formula
- CH2=CHCN
- Application
- Used in production of plastics (ABS, SAN), acrylic fibers, synthetic rubbers, and as a chemical intermediate
- HS Code
- 29261000
- Poisonous
- YES
- Shape
- Liquid
- Shelf Life
- 12 months in sealed containers under proper conditions
- Usage
- For industrial and chemical manufacturing use only
- Ingredients
- Acrylonitrile
- Appearance
- Clear, Colorless Liquid
- Molecular Weight
- 53.06 g/mol
- Solubility
- Slightly soluble in water; miscible with most organic solvents
- Product Type
- Organic Chemical Compound
- Grade
- Industrial Grade
About Acrylonitrile
Acrylonitrile (stabilised with hydroquinone monomethyl ether) for synthesis
| Order number | Packaging | Quantity | Price |
| AC27508 | Alu bottle | 100 ml | 13.05 |
| AC27508 | Alu bottle | 1 l | 22.725 |
| Product information | |
| Synonyms | Acrylic acid nitrile, Vinyl cyanide |
| Hill Formula | C3H3N |
| Chemical formula | CH2=CHCN |
| HS Code | 2926 10 00 |
| EC number | 203-466-5 |
| Molar mass | 53.06 g/mol |
| Storage | Store at +2°C to +8°C. |
| EC index number | 608-003-00-4 |
| CAS number | 107-13-1 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Ignition temperature | 480°C |
| Solubility | 73 g/l (20°C) |
| Melting point | -83.55°C |
| Molar mass | 53.06 g/mol |
| Density | 0.81 g/cm3 (20°C) |
| pH value | 6.0 - 7.5 (50 g/l, H2O, 20°C) |
| Boiling point | 77.3°C (1013 hPa) |
| Vapor pressure | 124 hPa (20°C) |
| Explosion limit | 2.8 - 28 %(V) |
| Flash point | -5°C |
| Refractive index | 1.391 (20°C, 589 nm) |
| Water absorption | 320 g/kg (20°C) |
|
| |
| Hazard Pictogram(s) |
|
| RTECS | AT5250000 |
| Storage class | 3 Flammable Liquids |
| WGK | WGK 3 highly water endangering |
| Disposal | 9 |
| Safety information | |
| R Phrase | R 45-11-23/24/25-37/38-41-43-51/53 |
| S Phrase | S 9-16-53-45-61 |
| Categories of danger | carcinogenic, highly flammable, toxic, irritant, sensitizing, dangerous for the environment |
| Hazard Symbol | Flammable |
| Transport information | |
| Declaration (transport by sea) IMDG-Code | UN 1093 ACRYLONITRILE, STABILIZED, 3 (6.1), I |
| Declaration (transport by air) IATA-DGR | UN 1093 ACRYLONITRILE, STABILIZED, 3 (6.1), I |
| Toxicological data | |
| LD 50 oral | LD50 rat 78 mg/kg |
| LD 50 dermal | LD50 rabbit 63 mg/kg |
| Specifications | |
| Assay (GC, area%) | 99 % |
| Density (d 20 °C/ 4 °C) | 0.805 - 0.807 |
| Water (K. F.) | 1.00% |
| Identity (IR) | passes test |
Key Properties and Applications
Acrylonitrile is distinguished by its volatility and distinctive bitter, unpleasant taste. Its industrial value chiefly lies in its utility for making plastics, acrylic fibers, and synthetic rubber. Used exclusively for industrial and chemical manufacturing, acrylonitrile acts as a vital precursor for products within automotive, textile, and consumer goods industries.
Safe Handling and Storage Guidelines
This substance mandates stringent handling due to its flammable and toxic characteristics. Store in sealed containers below 30C, away from heat, sparks, and open flames. Protective equipment must be worn to prevent inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact, and emergency response protocols should be in place for accidental exposure or spills.
FAQs of Acrylonitrile:
Q: How should Acrylonitrile be stored safely in an industrial setting?
A: Acrylonitrile must be stored below 30C in tightly sealed containers, away from heat sources, sparks, open flames, and incompatible substances such as strong oxidizers, acids, alkalis, and copper. Proper ventilation and adherence to recommended safety protocols are essential.Q: What are the primary industrial uses for Acrylonitrile?
A: Acrylonitrile is mainly used for manufacturing plastics like ABS and SAN, acrylic fibers, and synthetic rubbers. It also functions as a chemical intermediate in various chemical synthesis and industrial applications.Q: When is Acrylonitrile considered hazardous, and what are the specific health risks?
A: Acrylonitrile poses health hazards upon inhalation, ingestion, or skin absorption, potentially causing irritation and increased cancer risk. It is highly flammable and classified under Hazard Class 3, necessitating immediate precautions in case of spills or exposure.Q: Where does Acrylonitrile find its environmental impact, and how should spills be managed?
A: Acrylonitrile is harmful to aquatic life and requires proper containment and disposal protocols. In the event of a spill, evacuate the area, ventilate, contain the liquid, and follow local environmental regulations for cleanup and disposal.Q: What is the process of using Acrylonitrile in polymer production?
A: During polymer production, acrylonitrile acts as a monomer and is carefully polymerized, often with other chemicals, under controlled industrial conditions to produce plastics and fibers. The process is strictly regulated to avoid unwanted polymerization and hazardous reactions.Q: How does Acrylonitrile benefit industrial manufacturing despite its hazards?
A: Acrylonitrile enables the production of versatile plastics, resilient synthetic rubbers, and strong acrylic fibers, which are integral to automotive, construction, and textile industries, thereby contributing to innovation and product durability.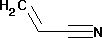

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
"Only deals in retail accepting orders upto 500ml only".
 |
ALPHA CHEMIKA
All Rights Reserved.(Terms of Use) Developed and Managed by Infocom Network Private Limited. |
 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese


 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry


