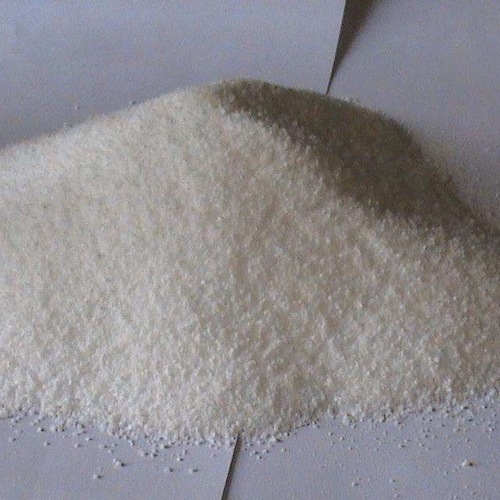
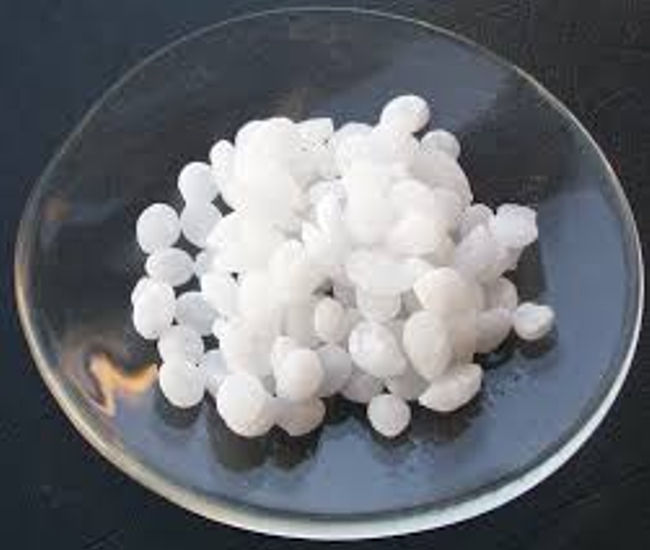
SODIUM HYDROXIDE pellets Extra Pure
Price 380 INR/ Kilograms
SODIUM HYDROXIDE pellets Extra Pure Specification
- Purity
- Extra Pure (Min. 99%)
- Ph Level
- Highly Alkaline (pH >13 in solution)
- Density
- 2.13 Gram per cubic centimeter(g/cm3)
- Boiling point
- 1390C
- Size
- Pellet Form
- Shelf Life
- 5 years if stored properly
- Physical State
- Solid Pellets
- Packaging Type
- Bottle, HDPE Jar
- Usage
- Used in chemical synthesis, titration, pH adjustment, laboratory reagent
- Molecular Weight
- 39.997 g/mol
- Molecular Formula
- NaOH
- Melting Point
- 318C
- Storage Instructions
- Store in tightly sealed container, in cool, dry place, away from moisture
- CAS No
- 1310-73-2
- Grade
- Laboratory Grade
- Type
- University Lab Chemicals
- Application
- Industrial, Laboratory
- Appearance
- White Solid Pellets
- Purity(%)
- Min. 99%
- Moisture Content
- <0.1%
- HS Code
- 28151110
- Solubility
- Soluble in water, alcohol and glycerol
- UN Number
- UN 1823
- Hazard Information
- Corrosive/Caustic; Causes burns
- EC Number
- 215-185-5
- Odour
- Odourless
- Reactivity
- Reacts violently with acids and water
SODIUM HYDROXIDE pellets Extra Pure Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 5 Kilograms
- FOB Port
- NHAVA SHEVA PORT MUMBAI MAHARASHTRA INDIA
- Payment Terms
- Cash on Delivery (COD), Cash Advance (CA), Cash in Advance (CID), Cheque, Delivery Point (DP)
- Supply Ability
- 50000 Kilograms Per Week
- Delivery Time
- Week
- Sample Policy
- Within a certain price range free samples are available
- Packaging Details
- 500GM, 1KG, 2.5KG, 5KG, 25KG, 50 KG export worthy Packing
- Main Export Market(s)
- Asia, North America, South America, Middle East
- Certifications
- CE CERTIFICATE, ISO 9001 2015, ISO 14001 2015, OHSAS 18001 2007, WHO GMP
About SODIUM HYDROXIDE pellets Extra Pure
Sodium Hydroxide Pellets Laboratory Reagent 500 Gram, Plastic Bottle.
Purity Percentage: 98%
CAS No: 1310-73-2
Synonyms (also called as) : anhydrous caustic soda / caustic alkali / caustic flake / caustic soda, solid / caustic white / caustic, flaked / hydrate of soda / hydroxide of soda / LEWIS red devil lye / soda lye / sodium hydrate / sodium hydroxide, pellets
Chemical State: Solid
Containers Type: Plastic
Chemical formula : HNaO / NaOH
COA or MSDS: Documents will be sent along with product
Storage Condition: Keep in a tightly closed container. Protect from physical damage. Store in a cool, dry, ventilated area away from sources of heat, moisture and incompatibilities. Always add the caustic to water while stirring; never the reverse. Containers of this material may be hazardous when empty since they retain product residues (dust, solids); observe all warnings and precautions listed for the product. Do not store with aluminum or magnesium. Do not mix with acids or organic materials."
Exceptional Laboratory-Grade Purity
These Sodium Hydroxide Extra Pure pellets are specially manufactured for laboratory and industrial use, offering a minimum purity of 99%. Each batch presents consistent results, making them ideal for chemical synthesis, titration, and laboratory reagents. Their high-grade quality ensures reliability for precise scientific and industrial processes.
Safety and Storage Precautions
Due to their highly corrosive and caustic nature, Sodium Hydroxide pellets must be handled with strict safety protocols. They should always be stored in tightly sealed containers, away from moisture, acids, and incompatible substances. Use appropriate personal protective equipment to avoid chemical burns. Proper storage extends shelf life up to 5 years.
Versatile Applications and Ease of Use
Sodium Hydroxide pellets dissolve easily in water, alcohol, or glycerol, producing highly alkaline solutions (pH >13). They are essential in chemical manufacturing, laboratory procedures, pH adjustments, and educational demonstrations. The solid pellet form allows for precise measurement and reduced dust compared to powders.
FAQs of SODIUM HYDROXIDE pellets Extra Pure:
Q: How should Sodium Hydroxide Extra Pure pellets be safely stored and handled?
A: Store the pellets in a cool, dry location within a tightly sealed HDPE jar or bottle, away from moisture and acids. Always use goggles, gloves, and lab coats when handling, as Sodium Hydroxide is highly corrosive and can cause severe burns.Q: What are the primary uses of Sodium Hydroxide Extra Pure in laboratories and industries?
A: These pellets are utilized for chemical synthesis, pH adjustment, titration, and as a standard laboratory reagent. Their high purity ensures suitability for analytical and research applications.Q: When should I add Sodium Hydroxide pellets to a solution during an experiment?
A: Always add Sodium Hydroxide pellets slowly to water (never the reverse), with constant stirring, to prevent violent reactions and splattering. Avoid adding to acids or moist environments directly.Q: Where can Sodium Hydroxide pellets be used in academic or research laboratories?
A: They are commonly used in chemistry laboratories for preparing alkaline solutions, performing titrations, saponification reactions, sample digestion, and neutralizing acids, as well as for instructional experiments.Q: What is the benefit of using the pellet form of Sodium Hydroxide over powder or flakes?
A: Pellet form minimizes dust exposure, allows more precise measuring, and reduces the risk of inhalation or accidental spills, making handling safer and cleaner.Q: Is Sodium Hydroxide Extra Pure soluble in alcohol or glycerol, and if so, how well does it dissolve?
A: Yes, the pellets dissolve readily in water, alcohol, and glycerol, forming clear, highly alkaline solutions suitable for a wide range of chemical and laboratory uses.Q: What precautions should be taken during the disposal process of Sodium Hydroxide solutions?
A: Neutralize the Sodium Hydroxide solution with a suitable acid to bring the pH to a safe level, then dispose of it in accordance with local environmental and safety regulations. Never pour large amounts into drains without proper dilution and neutralization.




Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in Laboratory Chemicals Category
1,5-DIHYDROXYNAPHTHALENE
Minimum Order Quantity : 25 Gm, Kilograms
Type : University Lab Chemicals
Grade : AR
Purity(%) : 98 %
Usage : Laboratory, Research, Chemical Synthesis
Storage Instructions : Store in a cool, dry place, tightly closed container
ACETO CARMINE solution
Type : Other, Solution
Grade : Laboratory
Purity(%) : ~98%
Usage : Staining of chromosomes & nuclei in microscopy
Storage Instructions : Store at room temperature, away from direct sunlight
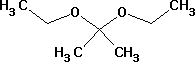
Diethoxypropane Chemical
Minimum Order Quantity : 500 Millimeters
Type : Industrial Lab Chemicals
Grade : Industrial
Purity(%) : 99.99
Usage : Lab Chemicals
Storage Instructions : Dry Place
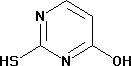
2 -Thiouracil
Minimum Order Quantity : 500 Milliliters
Type : Industrial Lab Chemicals
Grade : Industrial
Purity(%) : 99.99
Usage : Lab Chemicals
Storage Instructions : Dry Place
"Only deals in retail accepting orders upto 500ml only".
 |
ALPHA CHEMIKA
All Rights Reserved.(Terms of Use) Developed and Managed by Infocom Network Private Limited. |
 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese


 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry